
Social institutions examples & Definitions
Social institutions are organized and established ways of satisfying certain basic human needs. They are a system of social relations that become united by social rules and values. Social institutions are established patterns of behavior that define and structure social interactions within a particular society.
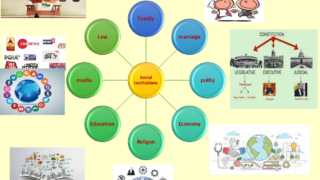
Social institutions examples
- The Family,
- Economy
- Polity
- Religion,
- Government,
- Education,
- The Economy, And
- The Legal System.
There are many different types of social institutions, each of which serves a particular purpose within society.
Social institutions are typically created to fulfill specific societal needs, such as
Family
This institution provides a framework for the raising of children, the socialization of individuals, and the provision of emotional and economic support.
Religion
This institution provides a framework for moral and ethical values, spiritual guidance, and community support.
Polity
This institution provides a framework for the regulation of behavior, the provision of public goods and services, and the maintenance of order.
Education
This institution provides a framework for the transmission of Culture, knowledge, skills, and cultural values from one generation to the next.
Economy
This institution provides a framework for the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Legal institution
This institution provides a framework for the regulation of behavior, the protection of individual rights, and the resolution of disputes.
Healthcare institution
This institution provides a framework for the provision of medical care, preventive health services, and the management of illness.
Media
This institution provides a framework for the production and dissemination of information, news, and entertainment.
Sports institution
This institution provides a framework for the organization and regulation of athletic activities, competitions, and events.
Social institutions has its own set of norms, rules, and values
Each of these institutions has its own set of norms, rules, and values that shape the way people interact with each other and influence the way society functions as a whole.
Social institutions can be formal or informal,
Social institutions can be formal or informal, and they develop around basic social trends and values that organize various activities that meet basic social needs.
These are often seen as the building blocks of society, as they provide the framework within which people live their lives and interact with each other. they play a crucial role in shaping the culture, values, and practices of a particular society.
Difference between organizations, associations and institutions
Social organizations
Social organizations are groups of people who come together for a specific purpose or goal.
Associations
A group of people who have come together for the purpose of achieving similar goals is called an association
Social institutions
.Institutions are organized and established ways of satisfying certain basic human needs.
Different scholar definitions of institutions
Ogburn and Nimkoff describe Social institutions are organized and established ways of satisfying certain basic human needs
Kingsley Davis defines An Institution may be defined as a set of interwoven folkways, mores and laws built around one or more functions.
Tischler, Wheaton, and Hunter describe “The ordered social relationships that grow out of the values, norms, statuses, and roles that organize those activities that fulfill society’s fundamental needs”
Horton and Hunt define “An institution is an organized system of social relationships which embodies certain common values and procedures and meets certain basic needs of the society.”
Social institutions are an essential aspect of any functioning society. They are a set of interrelated customs, policies, and rules that have been created to satisfy society’s basic needs.
In Marathi please click on next link :- सामाजिक संस्था म्हणजे काय | What Is Social Institution?
